
22 Sep 2019 HYN Himalayan Yoga Academy
Intro: Obesity
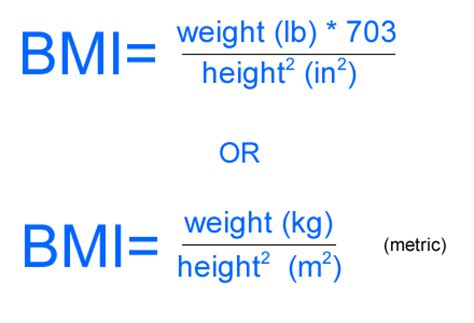
Obesity is the most common nutritional or metabolic disorder commonly defined by body mass index (BMI). It is a condition in which excess body fat accumulates to such an extent that health may be negatively affected. A BMI of 30 kg/m2 or higher is considered as obese. Body mass measurement criteria compare the weight and Height of the person to categorize him/her as overweight, pre-obese, or obese.
Obesity, in absolute terms, is an increase in body adipose tissue( fat tissue) mass. It is considered a chronic disease, like high blood pressure or diabetes. The foods we eat every day contribute to our well-being. Foods provide us with the nutrients we need for healthy bodies and the calories we need for energy. If we eat too much, however, the extra food turns into fat and is stored in our bodies. If we overeat regularly, we gain weight, and if we continue to gain weight, we may become obese.
Causes
A combination of excessive calorie consumption and a sedentary lifestyle are the primary causes of obesity. In a minority of cases, increased food consumption can be attributed to genetic, medical, or psychiatric illness. Excess fat accumulation may be due to an imbalance between energy intake and energy expenditure. There are no specific causes as such but the factors influencing are:
Diet:
Comsumption of high calorie and low –fibre diet
Sedentary Lifestyle:
A sendetary lifestyle plays a significant role in obesity.
Medical and psychiatric illness:
Certain physical and mental illnesses and the pharmaceutical substances used to treat them can increase the risk of obesity.
Socio-economic:
People of high socio-economic group are more prone to obesity.
Endocrine Factors:
Due to certain hormonal imbalance conditions like Hypothyroidism, Cushing Syndrome, etc.
Metabolism:
The persons whose rate of metabolism is low are at higher risk of obesity.
Water retention:
Too much consumption of tea, coffee , aerated drinks, soda soft drinks alcoholic drinks results in deposition of fluid in the body tissues and causes increase in weight.
Yogic Management of Obesity
- Om chanting and prayer
- Shodhana Kriya: Kapalbhati, Kunjal , Agnisara, Nauli
- Surya Namaskar
- Sukshma Vyayama: Selected Practices of Sukshma Vyayama: Udarasakti-vikasaka (2,3,4,6,7,8,9)
- Yogasanas: Tadasana, Katichakrasana, urdhwa, Hastottanasana, Dhanurasana, Uttan Padasana, Paschimotanasana, Asdha Matsyendrasana, Ushtrasana, Mandukasana, Shavasana
- Pranayama: Nadisodhana, Suryabhedi, Pranayama, Bhramari, Sitali and Bhastrika
- Special Practice: Yoga Nidra
- Dhyana: Om Chanting, Om meditation
- Yama and Niyama
Dietary Management
Prevention from Obesity
- Have regular meals at fixed interval
- Do not read or watch television while eating
- Try to keep healthy snacks at home like fruits, vegetables and sprouts.
- Do not keep nibbling between meals. Eat Slowly and chew the food properly
- Avoid drinking alcohol and smoking
- Encourage breast feeding to children as who gets proper breast milk has less probability of getting obesity
- Physical Activity
- Have control over carbohydrate intake
