
15 Jul 2023 HYN Himalayan Yoga Academy
Himalayan Yoga presents an article on Yoga Mudras to practice in daily life. Mudras have been a vital piece of profound practices in India and Nepal for millennia and have been portrayed in old Indian workmanship and models. In Hinduism, mudras are utilized in sanctuary customs and dance exhibitions. They are also found in practice in ritual dances and Buddha statues in Buddhism.
The starting points of yoga mudras can be followed back to old India and are referenced in old texts, for example, the Hatha Yoga Pradipika and the Gheranda Samhita, which date back to the fifteenth century CE. Be that as it may, what precisely is a yoga mudra? We should investigate.
What is Yoga Mudra?
In Yoga, mudras are viewed as non-verbal correspondences between the subtle body and the physical body, they are used to help stimulate the flow of energy through the body and activate specific areas of the brain to bring about a specific state of mind. They are often performed in pair with pranayama (breathing techniques) and asanas (yoga postures) to enhance the benefits that we receive as they channel the more energy flow in our body.
Mudras have a lot to offer in terms of spiritual, physical, and mental well-being, and are now widely used in yoga and meditation practice in the modern world. It’s also used in other forms of art, such as dance and music, due to its healing and therapeutic benefits.
7 Easy Yoga Mudras You Can Do every day
- Chin Mudra
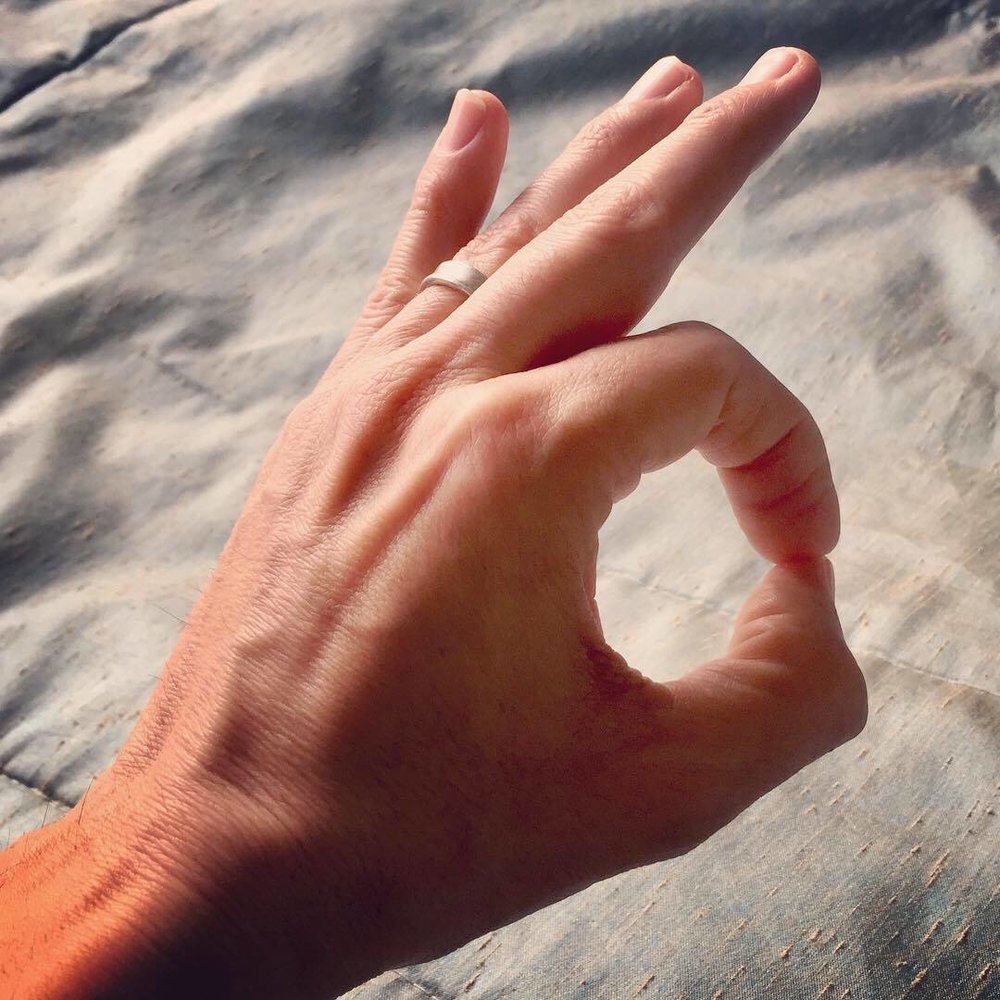

The Chin Mudra is much of the time utilized during contemplation and pranayama practices to assist with expanding concentration and focus. It is accepted to assist with adjusting the body’s energy stream and advance a feeling of quiet and peacefulness.
It is also used in asanas and yoga postures. The belief that one can transcend the ego and reach a higher level of consciousness by performing this mudra is represented by the union of individual consciousness and universal consciousness. It is frequently depicted in Buddha statues while he is meditating with his hands in Chin Mudra.
Steps of Chin Mudra:
- Sit in Sukhasana (Easy Pose), Padmasana (Lotus Pose), or Vajrasana (Thunderbolt Pose) in a comfortable seated position with a straight spine.
- Unite your hands before your chest, with your palms looking up.
- While keeping the other fingers straight, touch the tip of your index finger to the tip of your thumb. The other fingers remain extended while the index and thumb form a circle.
- Maintain this position while paying attention to your intention and breath. Relax and let go of any tension in your body by taking slow, deep breaths.
2. The Anjali Mudra

The Anjali Mudra is a common yoga pose that is performed at the beginning and end of classes as a gesture of respect and appreciation for the teacher and the practice.
This is the way to do the Anjali Mudra:
- Maintain a straight spine as you stand or sit in a comfortable position.
- Unite your hands before your heart, with your palms contacting and fingers facing up.
- Press your palms together solidly yet easily, ensuring your fingers are facing up and not twisted back.
- Stand firm on this foothold while zeroing in on your breath and your aim. Take slow, full breaths, and unwind.
- As you press your palms together, you can bow your head somewhat in a token of regard, modesty, and appreciation.
3. The Shuni Mudra
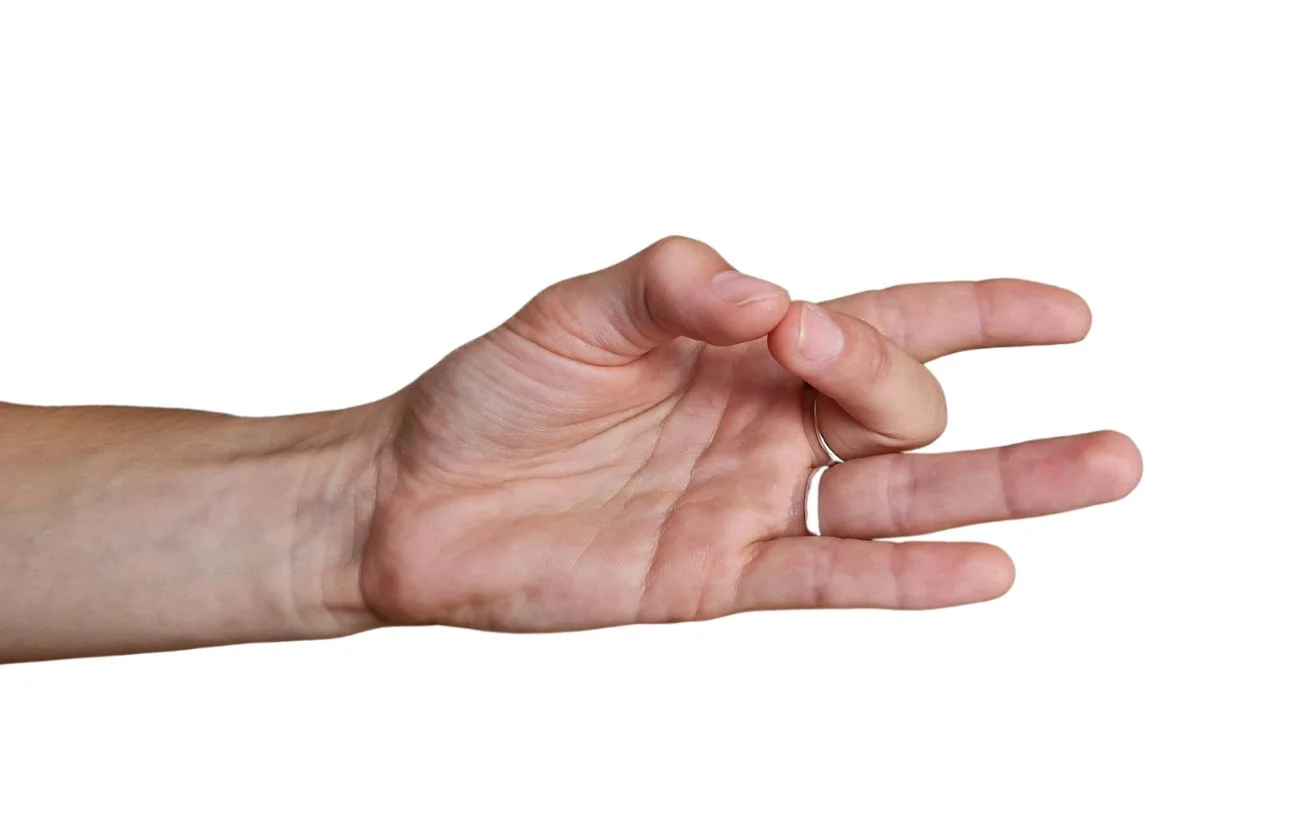

The Shuni Mudra is created by holding the other fingers straight and pressing the middle finger’s tip against the thumb. This yoga mudra is related to the component of earth and is accepted to expand the characteristics of persistence and assurance in the specialist, as well as the capacity to defeat impediments.
This is the way to perform Shuni Mudra:
- Sit in Sukhasana (Easy Pose), Padmasana (Lotus Pose), or Vajrasana (Thunderbolt Pose) in a comfortable seated position with a straight spine.
- Push your hands to the brink of collapse, with your palms looking up.
- Contact the tip of the center finger to the tip of the thumb, while holding different fingers straight. The other fingers remain extended while the middle and thumb form an energy circuit.
- Maintain this position while paying attention to your intention and breath. Relax and let go of any tension in your body by taking slow, deep breaths.
This mudra can be worked on during situated reflection, pranayama, and yoga asanas, yet in addition can be integrated into your day-to-day everyday practice whenever, for example, when you are feeling worried or have a troublesome undertaking ahead.
4. The Prithvi Mudra
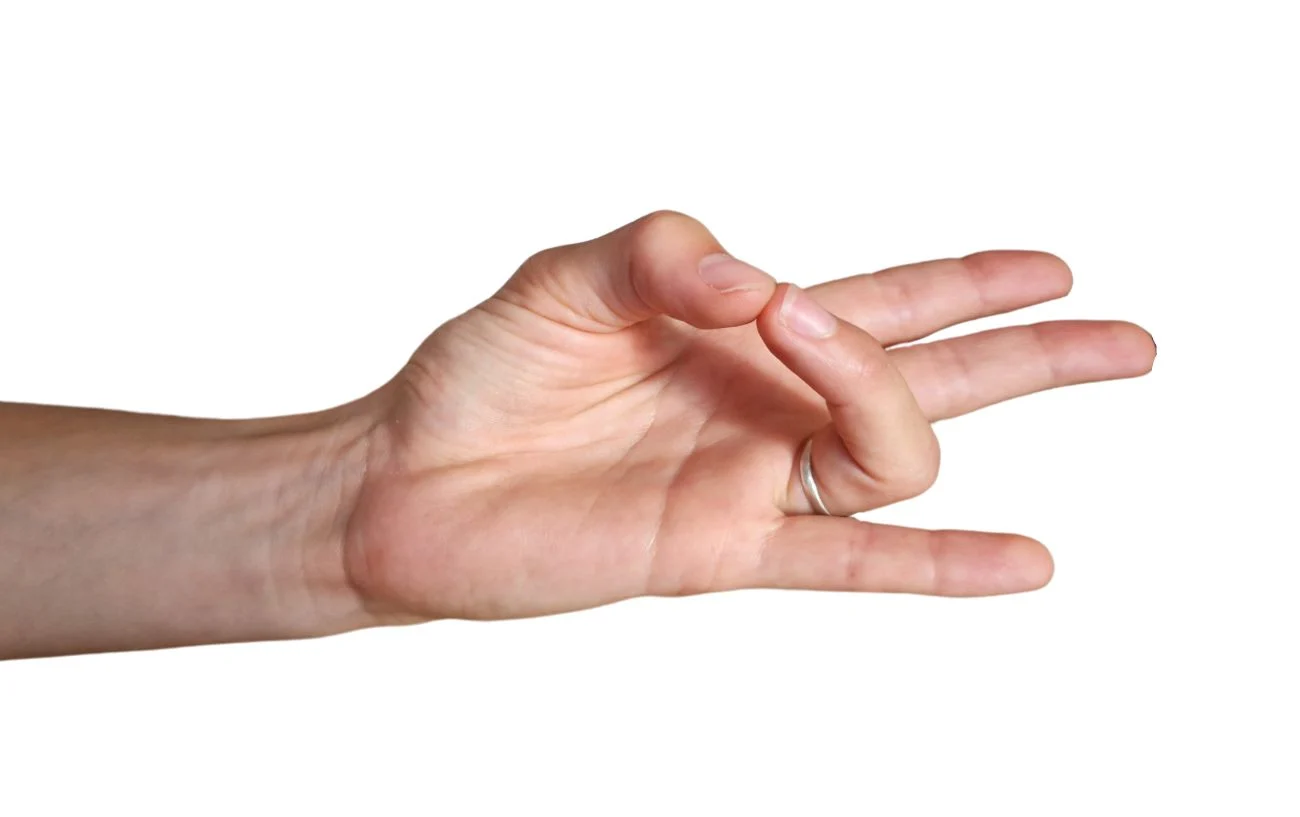

The Prithvi Mudra is created by holding the other fingers straight while touching the ring finger’s tip to the thumb’s tip. The earth element is associated with this yoga mudra, which is believed to aid in the body’s balance of this element, thereby enhancing overall physical strength and stability.
This is the way to perform Prithvi Mudra:
- Sit in Sukhasana (Easy Pose), Padmasana (Lotus Pose), or Vajrasana (Thunderbolt Pose) in a comfortable seated position with a straight spine.
- Push your hands to the brink of collapse, with your palms looking up.
- Contact the tip of the ring finger to the tip of the thumb, while holding different fingers straight. The ring finger and thumb structure a circuit of energy, and different fingers stay broadened.
- Maintain this position while paying attention to your intention and breath. Relax and let go of any tension in your body by taking slow, deep breaths.
Likewise with different mudras, Rehearsing Prithvi Mudra for no less than 5-10 minutes every day for ideal benefits is suggested. It tends to be worked on during situated reflection, pranayama, and yoga asanas and it tends to be remembered for your day-to-day daily schedule too.
5. Vayu Mudra

Vayu Mudra is framed by collapsing the forefinger and squeezing it against the foundation of the thumb. This mudra is related to the air component and is accepted to assist with adjusting this component inside the body, which can ease specific circumstances like clogging and weakness.
Vayu Mudra is performed as follows:
- Sit in an agreeable situated position with your spine straight.
- Push your hands to the brink of collapse, with your palms looking up.
- While maintaining straight fingers, fold the index finger and press it against the base of the thumb. The other fingers remain extended while the index and thumb form an energy circuit.
- Stand firm on this foothold while you center around your breath and your expectation. Take slow, full breaths, and let go of any strain in your body.
Vayu mudra is thought to be helpful for people who have constipation, indigestion, and gas, as well as for people who have asthma, COPD, and chronic bronchitis, which are respiratory conditions.
However, mudras should not be used in place of medical care, and if you have any questions about your health, you should talk to a doctor before beginning mudra practice. Mudras are viewed as a supplement to conventional clinical treatment and not a substitution for it.
6. The Apana Mudra
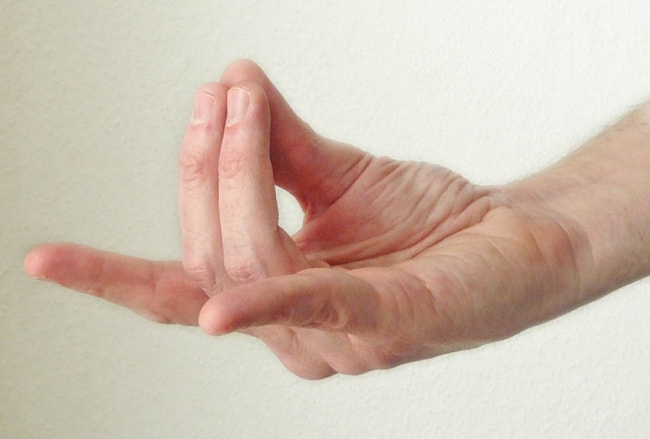

The Apana Mudra is shaped by collapsing the center and ring fingers and squeezing them against the foundation of the thumb while keeping different fingers straight.
Also known as Apana Vayu, it is used to help the body move energy downward, which is important for controlling the reproductive organs and getting rid of waste. This Mudra is accepted to help in the treatment of conditions like clogging, acid reflux, and gas, as well as specific circumstances connected with regenerative organs.
Apana Mudra is performed as follows:
- Sit in an agreeable situated position with a straight spine.
- Push your hands to the brink of collapse, with your palms looking up.
- Overlay the center and ring fingers and press them against the foundation of the thumb, while keeping different fingers straight. The center and ring finger and thumb structure a circuit of energy.
- Maintain this position while paying attention to your intention and breath. Take slow, full breaths, and unwind.
Apana Mudra, like all mudras, is thought to be more effective when practiced in conjunction with pranayama, visualization, and affirmation. Before beginning a mudra practice, it is essential to consult a medical professional as always.
7. The Surya Mudra
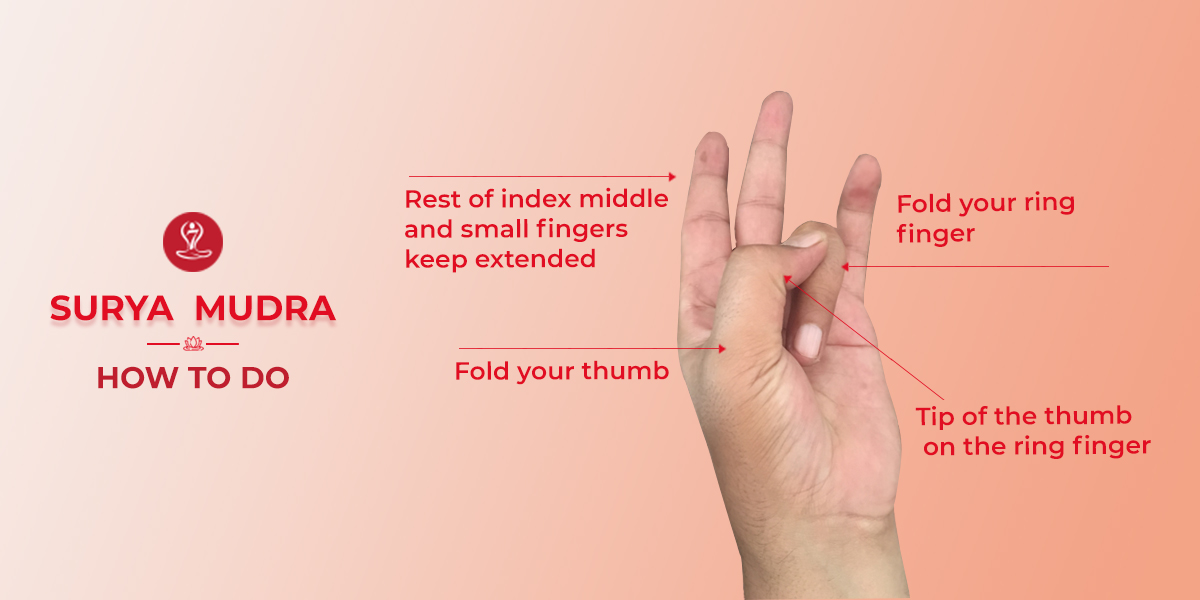
The Surya Mudra is created by pressing the ring finger’s tip against the thumb’s base while maintaining straight fingers. This yoga mudra is accepted to assist with adjusting the component of fire in the body and is many times used to build energy, and essentialness and to assist with weight reduction. It is utilized to actuate the Manipura Chakra, or the sunlight-based plexus, which is related to resolve, confidence, and the stomach-related framework.
Surya Mudra is performed as follows:
- Sit in Sukhasana (Easy Pose), Padmasana (Lotus Pose), or Vajrasana (Thunderbolt Pose) in a comfortable seated position with a straight spine.
- Push your hands to the brink of collapse, with your palms looking up.
- Press the tip of the ring finger against the foundation of the thumb, while keeping different fingers straight.
- Maintain this position while paying attention to your intention and breath. Relax and let go of any tension in your body by taking slow, deep breaths.
Conclusions for Yoga Mudras:
Yoga Mudras are a significant part of yoga practice and are accepted to have many advantages for both the body and the brain. In yoga, there are a variety of mudras, each with its own benefits and applications. Once more, Mudras ought not to be viewed as a substitute for clinical treatment. Mudras are viewed as a supplement to conventional clinical treatment and not a swap for it. Regardless, it’s fundamental to be aware of the unique situation and the beginning of the mudra while performing them to get the full advantages and figure out the appropriate use.
To develop your yoga information further then Himalayan Yoga Academy’s 200-Hour Yoga Teacher Training and 500-Hour Yoga Teacher Training Welcomes you invites you. Our advanced 500-Hour Yoga Teacher Training program will help you reach your full potential as a yoga practitioner and teacher. Our program in Nepal is designed to be safe, suitable, and transformative. It gives you a complete and authentic yogic experience while also immersing you in Nepal Immerse Culture and Natural Diversity.
