24 Sep 2019 HYN Himalayan Yoga Academy
Introdution:
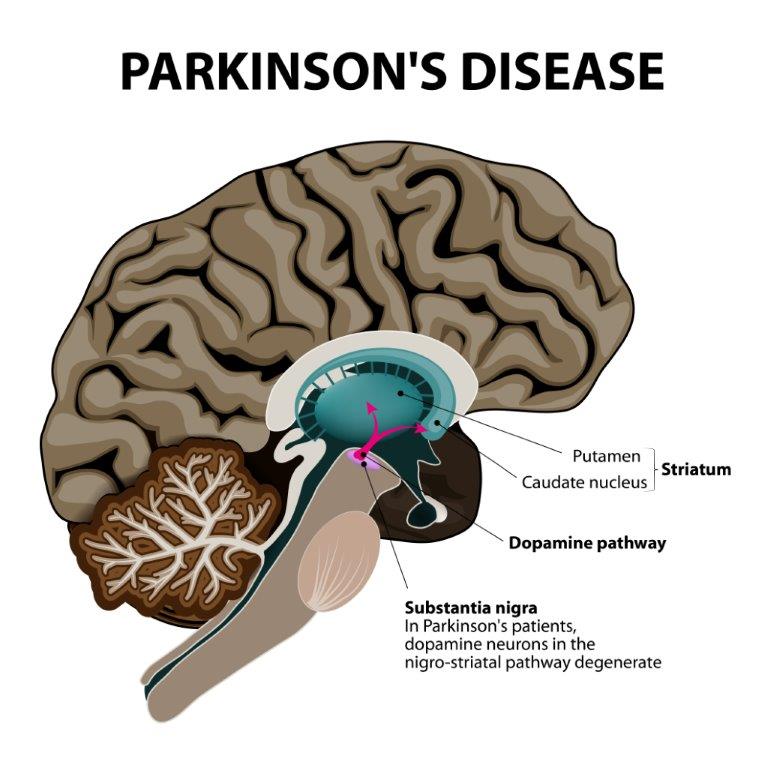
Parkinson’s disease is a degenerative disorder of the brain. Descriptions of Parkinson’s disease are present in the ancient Indian system of Medicine, Ayurveda. It is described as the disorder Kampavata. Parkinson’s disease belongs to a group of conditions called movement disorders. In this disorder, nerve cells or neurons in the brain that control muscle movements are greatly affected. It is characterized by loss of muscle control, which leads to trembling of limbs and head while at rest, stiffness, slowness, and impaired balance. This disease generally develops in elderly people of 50.
Sometimes Parkinson’s disease occurs in younger adults. It affects both men and women. The progression of Parkinson’s disease and the degree of impairment vary from individual to individual. Many people with this disease may live long productive lives, whereas others become disabled much quicker.
Causes:
- Genetic
- Excessive Stress
- Environmental Factors: Possible Toxins could include pesticides and herbicides used in farming, toxins released by industrial plants, air pollution related to road traffic.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption
- Any other neurological illness
- Drub Abuse
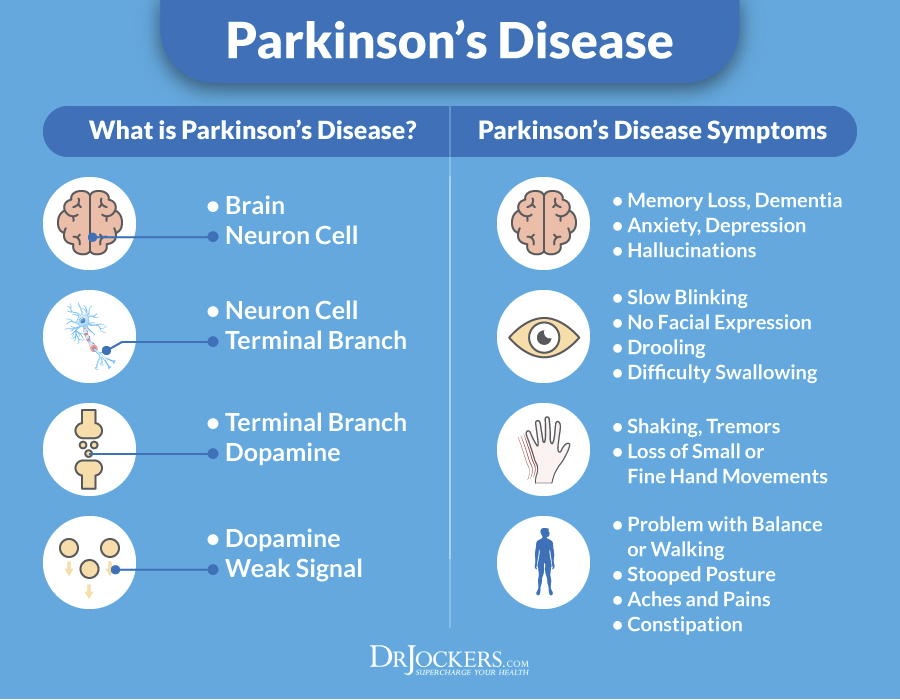
Sign and Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
1. Symptoms that affect motor functions
- Tremors: It is one of the most common symptoms. Trembling in fingers, hands, arms, feet, legs, jaw, or head. Resting tremors are noticeable when hands are at complete rest.
- Rigidity: This includes stiffness of the joints and when combined with tremor will produce a cogwheel type of rigidity when the limbs are passively moved.
- Akinesia or Bradykinesia: This slowness or absence of movement.
- Postural Instability:
- Shuffling Gait: While walking person takes small step with their feet barely leaving ground.
- Stooped Posture: In severe or progressive forms of Parkinson’s Disease, the person’s head or upper body may become bent at a right angle to the trunk.
- Dysphagia: The person may have difficulty in swallowing and this leads to aspiration some times.
2. Neuro-Psychiatric Symptoms affecting (mood, thinking and behaviour)
- Depression: Depression is thought to affect between 30-80 percent of all people suffering from this disease.
- Mild cognitive impairment: The person’s voluntary and involuntary responses will show a significant delayed reaction.
- Dementia: It will often occur in about 20-40 percent of all people suffering form Parkinson’s Disease
- Anxiety: Anxiety can also affect people with Parkinson’s Disease.
- Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia is thought to affect half of those with Parkinson’s Disease. They can include changes to the brain, side-effects of some of the medications used to treat Parkinson’s Disease.
3. Symptoms that affect autonomic nervous systems
- Problems with Urination
- Drooling:
- Erectile Dysfunction in Men:
- Constipation:
Management
Parkinson’s Disease is a chronic disorder that requires board-based management including patient and family education, support group services, general wellness maintenance, physiotherapy, exercise, and nutrition.
Complementary Treatment:
There are many modalities and nutritional supplements which can ease symptoms and improve quality of life. Patients must inform their physician about the over-the-counter medications herbs or other supplements. Exercise therapy can help support and tone the underrated muscles and give inflexible joints a better range of motion.
Yogic Managment :
The practices which are helpful in the management of Parkinson’s Disease:
- Kriyas: Jalaneti, Sutraneti, Kapalbhati
- Yogic SukshmaVyama: Buddhitatha Dhritishaktivikasaka, Medhashaktivikasaka, Manibandha Shaki vikasakakriya
- Yogic Sthula Vyayama: Urdhwagati, Rekhagati
- Yogasanas: Tadasana, Trikonasana, Hastottanmasana, Katichakrasana, Pawanamuktasana, Ushtranasana, Bhujangasana, Makarasana, Shavasana.
- Pranayama: Nadishodhan, Bhramari , Ujjayi and Sitali
- Meditation : Breath Awarness, Om Meditation or Guided Meditation focusing on the affected part.
- Yogic Diet: Alkaline food with less oil, salt and spice
